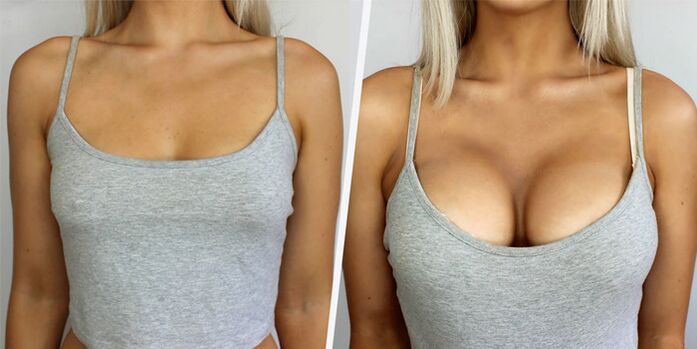
Shape correction, breast augmentation is one of the most popular procedures of plastic surgery. With the help of mammoplasty, you can correct congenital or acquired defects of the breast, restore its volume, elasticity after childbirth and breastfeeding. Properly performed surgery helps a woman become more attractive, more confident.
Indications for surgery
- Lowering and reduced elasticity of the mammary glands (mastoptosis).
- Increased breast volume while maintaining tone and position (macropathy).
- Decreased mammary glands after lactation.
- Small breast size (micromastia).
- Increased breast volume in men (gynecomastia).
Types of mammoplasty
- Increased mammoplasty(endoprosthetics) - breast augmentation, shape correction with implants. It is used after childbirth, breastfeeding, with congenital asymmetry.
- Reduction mammoplasty- Decreased bust size with mastoptosis or macropathy.
- Mastopexy- breast lift. It is indicated for mastoptosis if the breast volume meets the requirements for surgery.
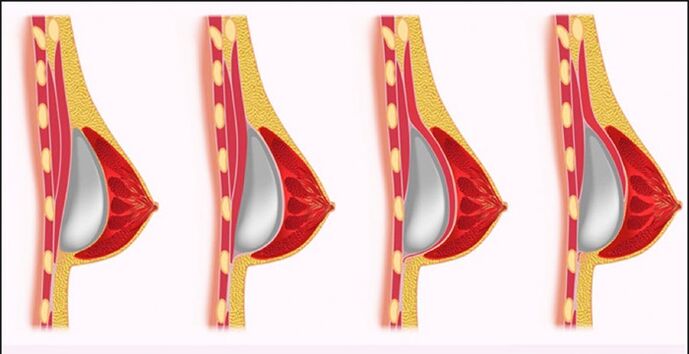
Endoprosthetics of the mammary glands
The operation involves the installation of silicone prostheses (implants) in the mammary glands. The choice of the place of the cut is in accordance with the woman. The implant is placed below the pectoral muscle, and if the volume of the breast allows, between the muscle and the mammary gland. The incision is sutured, no drainage is required. The nipple and areola enlarge after surgery.
Breast implants
Silicone or polyurethane endoprostheses correct the volume, the shape of the bust, give a feeling of natural body tissue.
The lifespan of implants exceeds 15 years, after which it is recommended to replace them.

The products differ in a number of indicators:
- Fillers: cohesive gels or saline (sodium chloride). The composition of the gels is more elastic, homogeneous, light, but dangerous for the body if it leaks. The salt solution is safer, softer and cheaper. Negative properties - murmur when moving, prone to leakage.
- Structure: rough (textured) or smooth. Textured implants are more stable, but skin folds can occur due to friction of body tissues against their surface. The disadvantage of smooth dentures is the likelihood of displacement.
- Shape: anatomical or round. The former have a more natural appearance, while the latter retain the symmetry and shape of the breast even when moved.
Reduction mammoplasty
When performing this type of surgery, the adipose tissue and breast tissue are partially removed, their size is changed and a new shape is obtained.
Cutting off excess tissue reduces the likelihood of cancer.
Possibilities of mammoplasty reduction:
- Liposuction. The method is considered conservative and leaves no seams. Designed for minor breast reduction with a mild degree of mastoptosis.
- Short (vertical) seam. A popular method in which the breasts maintain their natural shape and the nipples are sensitive. The operation takes little time, and the proportion of complications is small.
- T-shaped cut (anchor). The classic method, used to remove large amounts of tissue. Its disadvantages are the duration of recovery, a large scar.
- Amputation with nipple transfer. Used for very large breasts. The method is associated with a high risk of mammary gland injuries, loss of nipple sensitivity and inability to breastfeed.
Mastopexy
Breast lift without implants is possible in several ways:
- It is used vertically for mastoptosis of 1-2 degrees, the sutures are almost invisible, the cosmetic effect is long-lasting. The method is ineffective for lowering the breast by 3-4 degrees.
- Anchor mastopexy gives good results for ptosis of any complexity. Its disadvantages include a longer recovery period, noticeable sutures, an increased risk of breast tissue injury.
- Periareolar mastopexy is the removal of a small piece of skin around the areola. It is indicated for pseudoptosis, for other forms of bust relaxation it is ineffective.
Stages of work
High-quality medical care in all three phases is important for an excellent result of plastic surgery. The preparation period lasts 1-2 weeks. The surgery itself takes 1 to 4 hours.
Complete recovery occurs within 1, 5 months.
Preparations for mammoplasty

The operation is performed at the earliest one year after the end of lactation. 2 weeks before the operation, it is forbidden to take hormonal contraceptives, aspirin and preparations containing salicylates.
You should stop drinking alcohol, smoking.
In preparation, research is necessarily carried out:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- electrocardiogram;
- blood test for anticoagulants (coagulogram);
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands;
- general urine analysis
- testing for hepatitis and HIV viruses.
The course of surgical intervention
Bust plastic surgery is done under general anesthesia. A special type is the dermotension expander. It is used to increase breast volume with a lack of its own tissue and large implant sizes. The procedure is performed in 2 stages. First, an expander is installed to gradually stretch the breast tissue for 1, 5-2 months.
When the desired size is reached, the endoprosthesis is placed in the breast.
Operational cutting methods:
- Through the crease below the breast (submammary approach). A safe method to increase mammoplasty. The scar from the incision 4-5 cm long disappears over time under the slightly lowered breast. Access is difficult with micromastia in lean girls.
- Incision around or along the lower arch of the areola (periareolar approach). The advantage - surgical scars are almost invisible. This method is not recommended for patients planning breastfeeding due to the high risk of breast injury.
- Endoscopic augmentation via the axillary approach. High-tech equipment helps implant placement without damaging blood vessels and nerve fibers. An incision 3-4 cm long is made in the axillary zone, and then the scar is naturally masked. There is a limit on the volume of the implant - up to 400 ml.
- Endoscopic approach through the navel. This method is of little use due to the distance of the entry point from the site of surgery, the difficulty of forming a "pocket" for the prosthesis.
Rehabilitation after mammoplasty

If the operation passed without complications, the patient spends up to 3 days in the hospital. After discharge, it is necessary to attend dressing. Moderate pain in the area of the procedure that occurs in the first days is considered natural. The feeling of tightness of the skin is possible due to postoperative edema, which disappears after approximately 5-7 days.
After 4-6 weeks, the breast drops slightly, looks more natural and capsules form around the implant.
Rules for successful recovery:
- Do not load the shoulder girdle, do not lift weights.
- Do not visit fitness clubs, swimming pools, saunas, baths.
- Sleep on your back.
- Don't raise your hands.
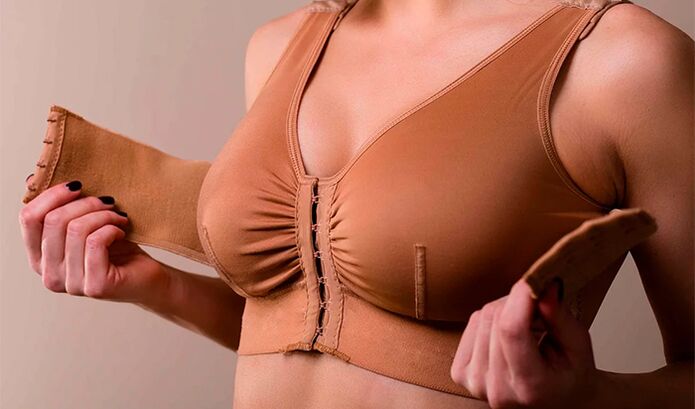
- After breast augmentation, be sure to wear compression clothing.
Possible complications
- Capsular contracture. The body forms a shell around the endoprosthesis, which can lead to its displacement, violation of the symmetry of the mammary glands and their hardening.
- Infection. Infection occurs during surgery due to violation of the rules of asepsis or after non-compliance with antiseptic standards of care. The period of special risk is 1 week after the operation.
- Keloid, hypertrophic scars. They appear if the body is predisposed to their formation. The formations look like dense ridges that rise above the surface of the skin and spoil the appearance of the breast.
- Accumulation of blood, serous fluid (hematoma, seroma) and, as a result, darkening of skin color. It occurs when blood vessels, lymph vessels are damaged during surgery or during the recovery period. The complication occurs due to low blood coagulation, a sudden rise in blood pressure, an endoprosthesis of the wrong size.
- Reduction or loss of sensitivity of the nipples, areola. It often occurs when large breasts are reduced by reducing mammoplasty due to nerve damage.
- Implant rupture. It is caused by a thin shell, which is often found in cheap dentures. The salt filler is easily absorbed by the body without causing harm. Damage to the endoprosthesis by cohesive gel is not always noticeable, but it is dangerous if silicone enters body tissues.
Breastfeeding after surgery

The safest procedure is through an incision in the armpit (transaxillary) or under the breast (submammary).
Approximately one year after surgery, breastfeeding is allowed.
Breastfeeding problems can occur in the following cases:
- The endoprosthesis is placed to compress the mammary glands, reducing the amount of milk they produce.
- An incision along the areola is more likely to injure the nerve endings around the nipple.
- Reduction plastic, associated with a reduction in breast size, interferes with the milk ducts and blocks their functions.
In which cases is breast plastic surgery contraindicated?
- Cardiovascular diseases, varicose veins (thrombophlebitis, thrombosis).
- Severe forms of mastopathy.
- Oncology.
- Blood clotting disorders, diabetes mellitus.
- Infectious diseases (ARVI, influenza).
- Neurological, mental disorders.
- Pregnancy, breastfeeding.
- Up to 18 years.
Advantages and disadvantages of mammoplasty
Advantages of plastic breast correction:
- Application of modern interventions.
- Correction of congenital and acquired mammary gland defects.
- Long-lasting and pronounced aesthetic effect.
- Short terms of operation.
- Ability to choose the shape, material of the endoprosthesis at will.
- Preservation of lactation ability.
Possible disadvantages include:
- Skin scars from cuts - sutures, scars (unless special absorbent materials are used).
- Danger of complications (infection, breast deformity, bleeding).
- The need to change endoprostheses every 10-15 years.
- High cost of mammoplasty.
- The need for general anesthesia.
- Painful feelings in the first postoperative days.
- The need to constantly wear compression underwear.
- Long period of rehabilitation (from several months to a year) with rejection of sports, physical activity, pregnancy, breastfeeding.


























